Elastomers are the soft, elastic materials, like gels and rubbers that are found in automobile and airplane parts, in sports equipment, and are used to protect precision machinery and buildings against vibrations. Scientists now want to make them thinner and tougher, without losing elasticity. Nagoya University materials engineer Yukikazu Takeoka and colleagues reviewed the most recent efforts towards improving elastomers for the journal Science and Technology of Advanced Materials.
Elastomers are made of many, long molecular chains of repeating subunits. They can undergo large deformations when stretched, returning to their original shape when the tension is released. They can do this because their molecular chains have enough mobility to stretch and crunch up.
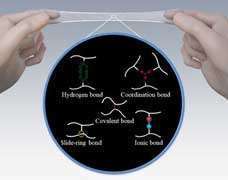
Elasticity and overall toughness depend on the interactions between the molecular chains inside the material. Scientists have been working on controlling how chains link together and interact in order to change elastomers’ mechanical properties.
Takeoka and his team explain that elastomers can be made tougher by introducing strong hydrogen or ionic bonds that can reversibly link elastomer chains together. These reversible bonds attach and detach from the elastomer chains as the material deforms. Scientists have used hydrogen bonds to fabricate strong hydrogels that can deform up to 600% and return to their original state within three minutes at 37 ° C or a few seconds at 50 ° C.
Elastomer chains can also be linked through ring-like ‘cyclic’ molecules, giving linked chains a large degree of flexibility and improved toughness. A team of scientists fabricated a very flexible elastomer by mixing solutions of polyethylene glycol and cyclic alpha-cyclodextrin in water.
The researchers suggest that further combining elastomers linked by reversible bonds and moving cyclic molecules could lead to even tougher elastomers with better elongation.
